Location: Japan
Partners: TotalEnergies, ISE Foods
Main activity: Distributed solar power generation
Commissioning: 2017

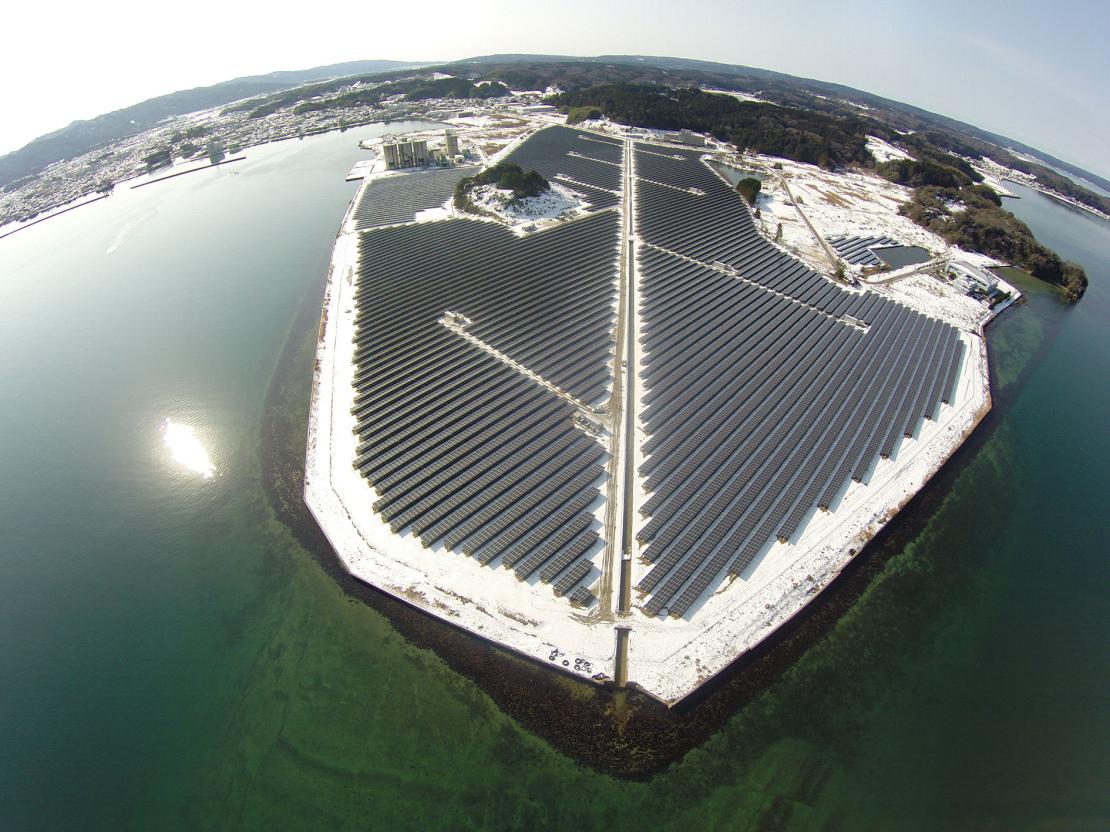
In March 2017, we started up our first solar power plant in Japan in Nanao, located on the Noto Peninsula on the country’s west coast. Built over 25 hectares, with a capacity of 27 MW, it generates enough power to serve 9,000 Japanese households through more than 80,000 high efficiency solar panels.
Japan is diversifying its energy mix, with TotalEnergies at its side! Since the 2011 Fukushima disaster and the ensuing shut-down of the country’s nuclear power plants, the Japanese government has introduced policies to encourage the development of renewable energies.
It was with this in mind that the Nanao PV power plant was built. The first TotalEnergies solar farm in Japan, it was constructed on brownfield land owned by the agri-food group ISE, a project partner.
The project is a technological marvel, mainly because of the geological and climate constraints. Located on the coast, the site is exposed to the risk of earthquakes and experiences heavy rainfall as well as strong winds and snow. The challenge was therefore to build a solar plant on a small site that could effectively generate power despite low levels of sunshine and withstand the elements for more than 20 years. We responded by using solar panels able to produce 45% more energy than conventional solar panels, meaning the plant achieves high output despite limited sunshine, which was crucial for the viability of the project.